Carbon farming helps reduce your carbon footprint
Carbon farming, as we have seen, reduces GHG emissions and stores carbon, which are essential to Australia’s response to climate change.
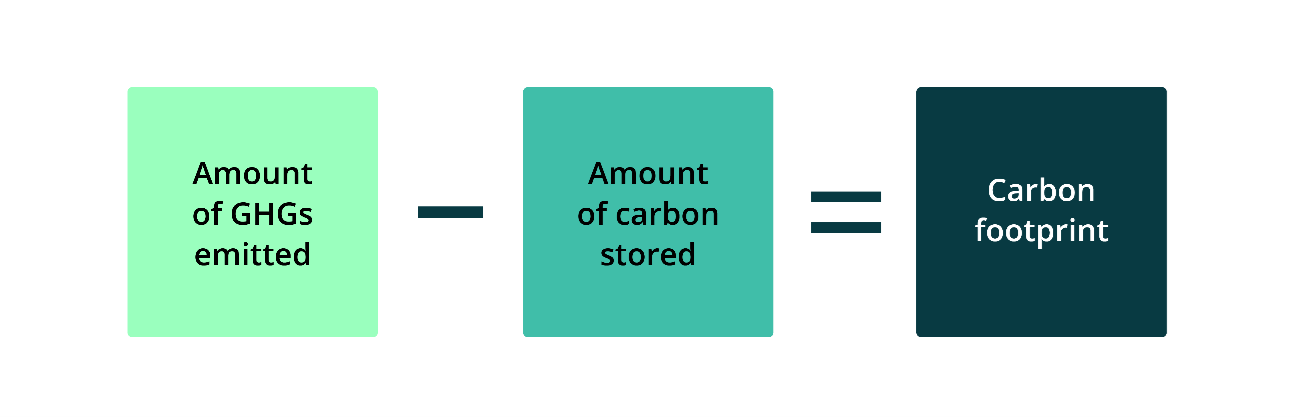
A ‘carbon footprint’ or ‘greenhouse gas footprint’ is the amount of GHGs emitted minus the amount of carbon stored by, for example, a farm, region or country.
Reducing your carbon footprint
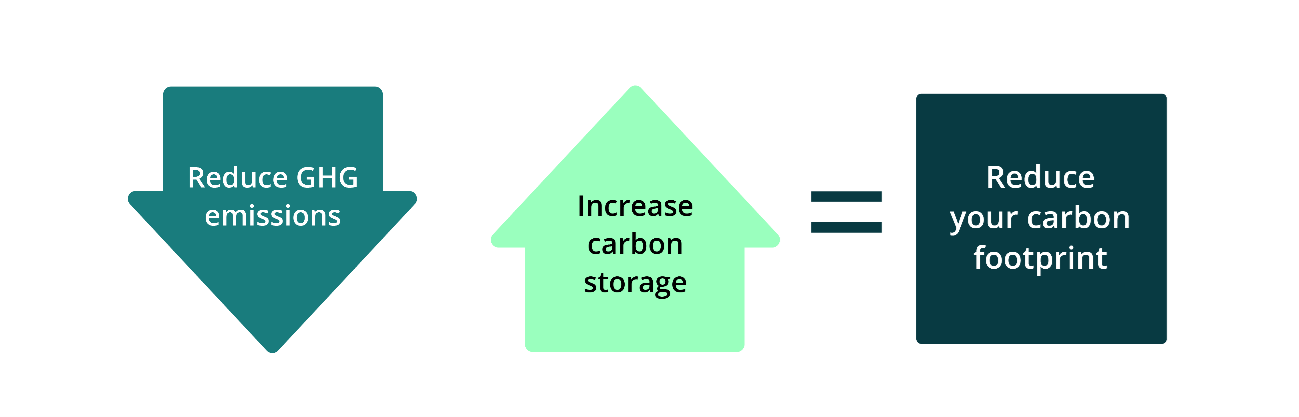
Reducing GHG emissions, storing more carbon or both helps reduce a farm’s or land area’s carbon footprint.
Knowing your carbon footprint
Getting serious about carbon farming means drilling down into detail to calculate your GHG emissions and carbon stored.
Topic 3 looks at some of the many calculators and tools available from governments, industry bodies and others to estimate GHG emissions and carbon storage.
Climate change and Earth’s increasing emissions
Human activities are causing increasing amounts of GHGs in the atmosphere.
Earth’s GHG emissions are mainly the result of:
- the burning of fossil fuels — the ancient remains of plants and animals that geological processes have transformed into carbon-rich coal, oil and gas — releasing carbon stored for millions of years into the air as carbon dioxide
- a range of human activities that release methane and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere.
The clearing of forests contributes to emissions and reduces Earth’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide.
The greenhouse effect

The Earth is heated by the sun, and some solar energy is reflected from its surface. GHGs prevent the loss or escape of heat into space, just as glass traps heat inside a greenhouse. This warming is essential for life on Earth. However, an increasing blanket of GHGs is trapping too much heat, preventing it from radiating back into space. This results in excessive global heating, which has consequences including changing climate patterns, upward-trending temperatures, melting ice, rising sea levels and extreme weather events, including droughts, floods, cyclones, and bushfires.
To learn more about climate change, read Understanding climate change.
Two resources for farmers to better understand how climate change is likely to affect their area and products are:
- My Climate View, which provides tailored climate overviews about what to expect from the climate at the user’s nominated location in the future and the climate impact on selected commodities
- Climate change impacts and adaptation on Australian farms, which presents the latest modelling by the Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences (ABARES) that examines the effect of recent and possible future climate changes on the profitability of Australian farms.
Other resources about climate change include:
- the Australian Government Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW) Climate change website which has information about climate science and adaptation, Australia’s climate change strategies, emissions reduction and reporting and other climate change topics
- Climate Change in Australia which provides climate information, projections, tools and data to help in understanding and planning how to adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Some states also have climate change adaptation plans. An example is the AdaptNSW website, which has information about actions to adapt to climate change by region.
<< 1.3. Carbon farming is good for business, good for the environment and Country