Carbon farming
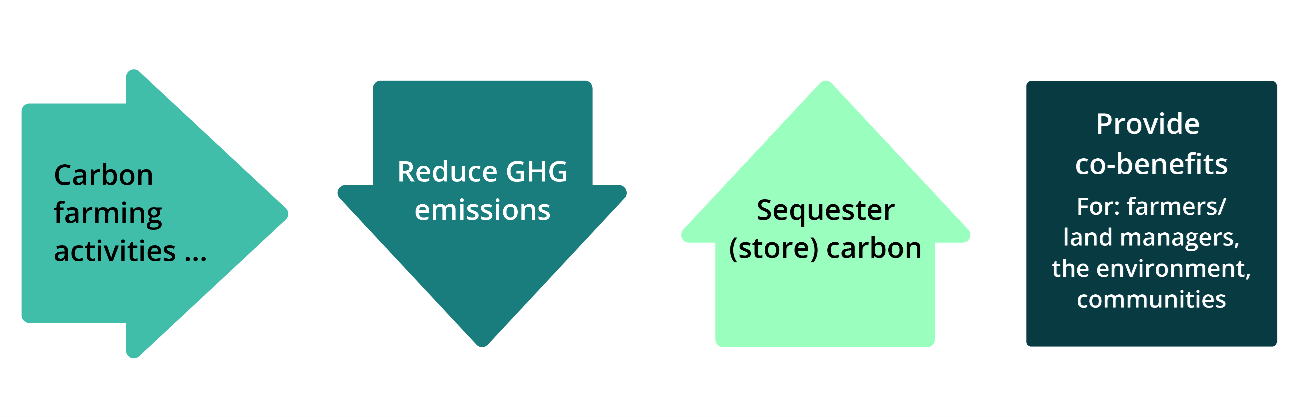
'Carbon farming' describes agricultural and land management activities that help mitigate climate change by:
- reducing emissions of the main GHGs: methane, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide, by avoiding or minimising them
- storing more carbon — also called sequestering carbon — which means capturing and removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing carbon in 'carbon sinks': vegetation and soil. Carbon is stored in land and coastal ecosystems (such as mangroves).
Each carbon sink stores carbon differently. For example:
- in vegetation (such as trees and grasslands), carbon is stored in the stems, trunks and roots
- in soil, carbon is stored in living and dead organic material.
Topic 2 looks at the carbon farming activities in the following table.
| Group | Activity |
|---|---|
| Soil | Conservation and strategic tillage Crop and pasture management Efficient fertiliser use |
| Livestock | Reduce beef and dairy cattle and sheep methane emissions Manage piggery and dairy effluent Grazing management |
| Vegetation | Afforestation Reforestation Agroforestry Retain existing native vegetation |
| Blue carbon | Restore wetlands, saltmarsh and seagrass Remove or modify barriers to tidal flow |
| First Nations traditional ecological practices | Cultural burning, including savanna fire management |
<< 1.1. Overview and learning outcomes
>> 1.3. Carbon farming is good for business, good for the environment and Country