PLANT PEST

Blomme et al. 2017.
Blood disease and moko disease
Exotic to Australia
Features: Banana-infecting bacterial wilt diseases with infected plants showing striking symptoms, the leaves wilt, the fruit rots on the inside becoming inedible, and the plant dies.
Where it’s found: Blood disease: Asia. Moko disease: Central and South America, North America, Africa, and Asia.
How it spreads: Long distance via infected plant material and over short distances by insects, birds, bats, tools, soil, and water.
At risk: All varieties of bananas (including plantains) and Heliconia species are susceptible to infections of this disease.
Keep it out
Blood disease and moko disease is caused by disease bacterium from the Ralstonia family. These bacterial diseases cause internal fruit discolouration and invade the vascular tissue of banana plants causing them to wilt.
Blood disease and moko disease of bananas cause significant levels of crop loss in the countries where they occur. The diseases when established spread readily in commercial setting by insects, tools, birds and bats.
These diseases threaten the Australian banana industry and home-grown bananas.
Importing goods
To keep blood and moko disease out of Australia, never ignore Australia’s strict biosecurity rules.
Import shipments may need to be treated and certified, so before you import, check our Biosecurity Import Conditions system (BICON).
What to look for
Blood disease and moko disease cause yellowing and wilting of leaves. Infected leaves die and form a skirt around the plant stem. The banana plant wilts and dies.
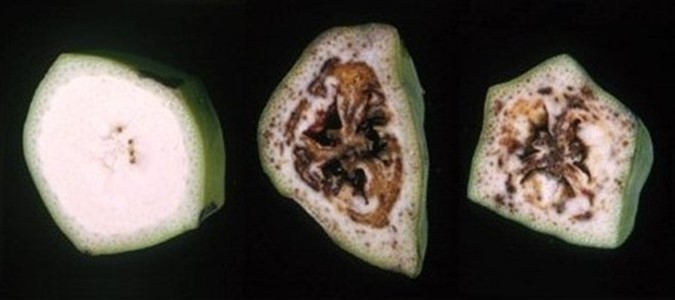
Banana fruit may not appear externally to be infected, however when banana fingers are cut transversely, a red-brown dry rot of the fruit pulp is seen. Banana flowers when infected blacken or shrivel.
The internal plant symptom of blood disease is a red-brown discolouration of the vascular tissue. The discolouration extends throughout the infected banana plant.
Bacterial ooze from cut infected plant stems can vary in colour from milky to yellow to reddish-brown to black. This ooze is also seen in infected heliconias.
H.D. Thurston
H.D. Thurston

Where to look
Importers
To keep blood and moko diseases out of Australia, never ignore Australia’s strict biosecurity rules.
Import shipments may need to be treated and certified so before you import, check our Biosecurity Import Conditions system (BICON).
Nursery owners, growers and home gardeners
Look for yellowing and wilting of leaves, which die and can form a skirt of dead leaves around the plant stem. Younger leaves may turn yellow before dying. Eventually the whole plant takes on a wilted appearance. Symptoms also include internal fruit discolouration and a bacterial ooze from cut stems.
What to do
If you think you’ve found blood or moko disease:
- take a photo
- do not disturb infected plants (this may be as simple as closing the doors on a shipping container or preventing access to a part of the plantation).
Read the detail
- Plant Health Australia: Moko Fact Sheet
- Plant Health Australia: Blood disease Fact Sheet
