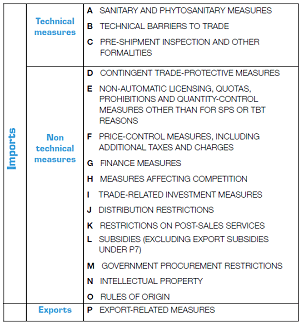
Non-tariff measures (NTMs) are requirements other than ordinary tariffs that can have an economic effect on international trade by influencing quantities traded, prices, or both.
Goods exported by Australian agriculture and food producers must meet these NTM requirements for an importing country to accept them. They typically include health and safety certification or biosecurity compliance measures.
All countries that trade, including Australia, apply NTMs. These measures help facilitate and regulate international trade.
Importing country requirements
It is important for Australian agricultural producers and exporters to understand country-specific NTMs and to make sure their goods comply with importing country requirements.
NTMs applied by importing countries:
- ensure imported products are safe and healthy for consumers
- protect countries from harmful pests and diseases that imported goods could carry
- help producers meet specific customer requirements.
Meeting non-tariff measures
For Australian producers and exporters, NTMs are a normal part of doing business. They can be applied in different ways and at different stages of the supply chain.
Commercial requirements may also apply in addition to NTMs. Although they are not written into law, these requirements can help Australian producers differentiate their products in international markets, and meet the preferences of consumers and manufacturers, as well as specific quality standards.
NTMs are used by countries, including Australia, for a range of reasons, including protecting biosecurity and consumer safety.
Where NTMs are seen to be a barrier to trade, we work with industry to consider how to best address them.
Find out more about meeting NTMs by contacting your relevant peak industry organisation or email our NTM team.
Wheat
Australian grain farmers follow best practice to meet importing countries’ NTMs and deliver high quality produce around the world.
Table grapes
Australian farmers are known for producing high quality table grapes and uphold high standards in food safety and quality assurance.
Ensuring grapes are free of contaminants, and that all fruit has been treated appropriately, are types of government-regulated NTMs, which ensure that produce is safe for consumers.
Most importing countries legitimately use NTMs to ensure that products are safe and free from pests and diseases.
Our farmers understand and respect the role of NTMs, which form an important part of the supply chain, and are an everyday part of doing business.
Farmers also strive to meet commercial requirements, such as ensuring that grapes are presented in a way that best shows off their natural colour. This commercial decision is not an NTM.
Oysters
Australian seafood exporters meet importing country NTMs by delivering safe, fresh oysters to overseas markets. Australian oyster farmers meet many NTMs every day by ensuring that oyster-growing stock is clean and disease-free for domestic and international markets. Growers also strive to meet commercial requirements such as grading oysters by size and shape. Australia's oyster farmers understand and respect the role that science-based and transparent NTMs play in our export supply chain
Wine
Australia is a leading international producer and exporter of wines. It is vital that Australian winemakers meet the NTMs of importing countries.
We work with industry to ensure NTMs are fair and reasonable so we can continue to deliver our award-winning wine to markets around the world.
Requirements such as bottle and package labelling are common and important NTMs. Likewise, wine exports need to comply with importing country food safety requirements for chemical residue limits and use of additives.
These NTMs are important steps, not only in international markets, but in the domestic market as well.
Wine producers may also need to meet commercial standards relating to vintage and variety, which are independent of government NTMs.
Sugar
Australia’s reputation as a sugar exporter is due to its high-quality produce and ability to meet market and importing country requirements.
With a large amount of sugar entering into international markets, it is vital that producers meet the NTMs of importing countries.
NTMs are an important part of the supply chain for the export of raw sugar.
Measures, such as testing for sugar purity and quality, allow importing countries to be certain that the product they are receiving is of a high quality and meets strict safety standards.
Australia's sugar millers also strive to meet commercial requirements such as providing customers with the correct sucrose percentage for the raw sugar's end use.
Wool
The superior quality of Australia’s wool exports means it is in high demand around the world.
The export of wool to the European Union, for example, requires that wool must originate from a country that is foot-and-mouth disease free.
NTMs such as freedom from disease are part of business-as-usual activities, which all of Australia's wool producers follow when farming high-quality wool.
When selling fine wool to the EU for high-quality clothing products, wool producers seek to meet commercial requirements for minimum quality standards and ensure that wool is traceable to the farm of origin.
Improving and expanding market access for Australia’s agricultural exports is vital. More market access supports a vibrant and competitive agricultural industry.
We run an ongoing program of market access achievements. We also manage a network of agricultural counsellors in key overseas markets.
This is an ongoing process and our core business.
Learn more about the whole-of-government Non-Tariff Barrier Action Plan for information on when NTMs can act as a barrier to trade.
See a summary of Australia’s involvement in disputes currently before the WTO.
Non-tariff measures and barriers to trade
The World Trade Organization (WTO) provides guidelines for applying NTMs.
The WTO rules state that NTMs must be:
- transparent
- not overly restrictive to trade
- not applied arbitrarily.
These rules help distinguish legitimate policy regulations and procedures from protectionist measures that may impede trade.
Most NTMs are reasonable and adhere to international standards for the trade of goods.
The Australian Government supports the WTO rules.
Sanitary and phytosanitary measures and technical barriers to trade
NTMs on food and agricultural products are predominantly:
As of 30 June 2018, SPS and TBT notifications make up over 86 per cent of all NTMs reported through the WTO, the majority of which relate to the trade of agricultural commodities.
NTMs also include measures such as:
- quotas
- subsidies
- price control mechanisms
- other measures outlined in the UNCTAD non-tariff measure classification system.
These measure can have an economic impact on trade by reducing access to markets and competitiveness.
Country-specific Technical SPS and TBT requirements are available in the Manual of Importing Country Requirements (Micor).
Exporters must meet these requirements for overseas countries to accept their products.
Priority non-tariff measures
In some cases, an NTM may be inconsistent with WTO rules and will act as a barrier to trade for Australian agricultural food exports.
The Australian Government is working with industry to address NTMs that are unfair, or impose unnecessary barriers to trade.
If an NTM is identified as constraining trade, the Australian Government and industry may:
- put a commercial solution in place to minimise impacts of meeting importing requirements
- hold bilateral discussions with the importing country to negotiate a solution
- seek resolution through appropriate international forums (for example, international standard setting bodies, SPS and TBT committees or WTO dispute settlement processes)
- use mechanisms through Free Trade Agreements to engage importing country governments.
Universal classification system
To help identify and quantify NTMs, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has developed a universal classification system (see Table 1). These measures reflect tools for regulation used in international trade environment.