Australia’s forests and forestry glossary
Timber
Wood products, usually square or rectangular in cross-section, milled from logs and that conform to industry grades, standards or specifications.
Traditional Owner
An Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander group, people or community with traditional ownership of an area of country that has clear boundaries from the country of other groups. Traditional Owners have common social, cultural and spiritual affiliation and responsibility for their land, and usually have rights to access and guide the management of that land.
See Indigenous (of people), Indigenous estate (land or forest).
Transpiration
Tree
A perennial plant with a self-supporting woody stem or trunk which usually develops woody branches. Also applied to multi-stemmed eucalypt mallees.
See Mallee.
Tree crown
See Crown (tree).
Tropical forest
Forests found in regions close to the equator characterised by high regular rainfall, and with a closed canopy of trees.
Turbidity
The degree to which the clarity of water is reduced by suspended solids, silt, sediments or organic matter.
Understorey
Layer or layers of vegetation beneath the main canopy or overstorey of a forest.
See Canopy, Overstorey.
Uneven-aged forest
Forest with trees of more than one age or age class present on the same site.
See Even-aged forest.
Unplanned fire
Fire started naturally (such as by lightning), accidentally, or deliberately (such as by arson), but not in accordance with planned fire management prescriptions. Also called bushfire or wildfire.
See Planned fire.
Unresolved tenure
Land where data are insufficient to determine land ownership status.
One of six land tenure classes used to classify land in the National Forest Inventory.
Urban forest
Broadly, a forest or an area of trees growing in an urban area, such as a city, town or suburb.
Urban forestry
The management of forests, areas of trees and individual trees in urban communities for the benefits provided to society.
Value-adding
The process of converting timber or forest products into one or more higher-value products.
Variable retention
A native forest silvicultural system alternative to clearfelling, that is designed to meet both harvest objectives and ecological objectives through the retention of trees within an area planned for harvest, with the amount and configuration of retention dependent upon the silvicultural objectives for the stand.
See Aggregated retention, Clearfelling, Harvesting, Silvicultural system.
Vascular plant
A plant with conducting tissue (comprising xylem and phloem) that transports water, mineral salts and sugars. Includes clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants).
See Angiosperm, Gymnosperm, Non-vascular plant, Phloem, Xylem.
Vegetation community
A group of plant species inhabiting a particular area and interacting with each other, especially through biotic relationships, relatively independently of other plant communities.
Veneer
Thin sheets of wood, usually thinner than 3 millimetres, which can be glued and pressed to make plywood, or glued and pressed onto core panels (typically wood, particleboard or medium-density fibreboard) to produce panels. Can be produced by slicing or peeling logs.
See Fibreboard, Particleboard, Peeler log, Plywood, Rotary peeling, Veneer log.
Veneer log
A log suitable for producing sliced veneer sheets. Excludes peeler logs used to produce rotary-peeled veneer.
See Peeler log, Veneer.
Vulnerable species/ecological community
A native species/ecological community facing a high risk of extinction in the wild in the medium-term future. One of the categories of threatened species/ecological communities defined in the Commonwealth Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
See Critically endangered species/ecological community, Ecological community, Endangered species/ecological community, Extinct, Extinct in the wild, Threatened ecological community, Threatened species.
Water quality
A property of water derived from the level of nutrients, particles and chemicals contained in water. Low levels of these components are associated with high water quality.
Water yield
The amount of water that flows out of a catchment (drainage basin).
See Catchment.
Watercourse
A natural or artificial water drainage channel. A watercourse may carry surface water flows intermittently or permanently.
Watershed
The dividing line between two catchments (drainage basins).
See Catchment.
Watertable
The underground level at which the ground is saturated with water, where the water pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure.
Wet forest/wet sclerophyll forest
Typically, eucalypt-dominated sclerophyll forest (not dry forest or rainforest) associated with moist (mesic) conditions, and with an understorey (if present) dominated or co-dominated by rainforest species or non-sclerophyll shrubs.
See Dry forest/dry sclerophyll forest, Eucalypt, Rainforest, Sclerophyll, Understorey.
Wetland
Areas of swamp, marsh, fen, peatland or mangrove, whether natural or artificial, and permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, and fresh, brackish or salt.
Forest wetlands are wetland ecosystems where forests are present.
See Mangrove.
Wild harvest
Commodity or product harvested from the wild, including farming of wildlife and feral animals.
Wilderness
Land that, together with its plant and animal communities, has not been substantially modified by, and is remote from, the influences of European settlement, or is capable of being restored to such a state; is of sufficient size to make its maintenance in such a state feasible; and can provide opportunities for solitude and self-reliant recreation.
Wildfire
See Bushfire.
Wildlife corridor
An area or strip of suitable habitat connecting wildlife populations otherwise separated by human activities.
See Connectivity, Fragmentation.
Wildling
A plant of a plantation tree species that has grown independently in forest or land adjoining the plantation.
Windthrow
Trees uprooted or broken as a result of severe wind associated with storms; the process of uprooting or breaking trees in this way.
See Disturbance.
Wood
The hard, fibrous, underbark component of the stem and/or branches of a tree, often suitable for conversion into products.
Woodchips
Small chips of wood produced from logs for use in fibre products or for conversion to pulp for paper manufacture.
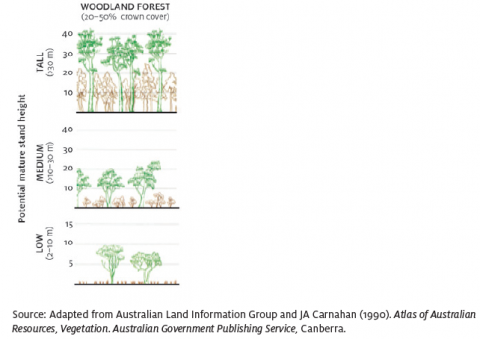
Woodland forest
As a National Forest Inventory cover class, native forest in which the tree crowns cover between 20% and 50% of the land area.
See Closed forest, Crown cover, National Forest Inventory, Open forest, Sparse woody vegetation.
Click here for an enlarged version.
World Heritage
Areas deemed to have outstanding universal value for humankind under an international convention (the World Heritage Convention) to which Australia is a signatory.
Xylem
A tissue in vascular plants that transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients upwards from the roots. Secondary xylem forms the woody component of trees.
See Cambium, Phloem, Vascular plant, Wood.
Yield association
A grouping of forest types that display similar commercial attributes of merchantability and productivity.
See Merchantability, Productivity.
